文章转载自 数据结构——堆(带图详解)_大根堆-CSDN博客 ,有删改
目录
堆 (Heap)
堆的概念
前面介绍的优先级队列在JDK1.8中其底层使用了堆的数据结构,而堆实际就是在完全二叉树的基础之上进行了一些元素的调整。
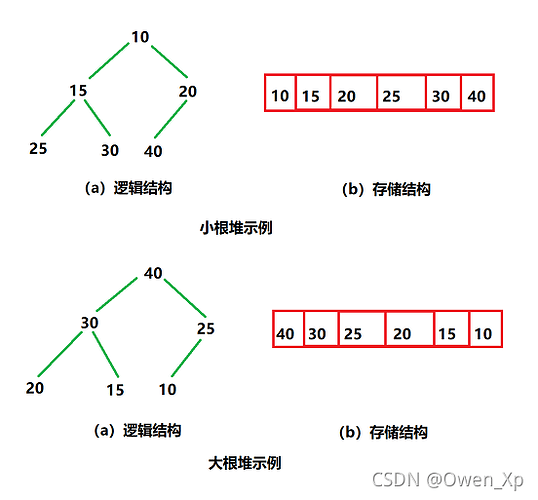
如果有一个 关键码的集合 K = {k0 , k1 , k2 , … , kn-1} ,把它的所有元素 按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一 个一维数组中 ,并满足: Ki <= K2i+1 且 Ki<= K2i+2 (Ki >= K2i+1 且 Ki >=K2i+2) i = 0 , 1 , 2… ,则 称为小堆 ( 或大堆) 。(即双亲比孩子的数值小(大)——小(大)堆)将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆的性质
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
下面来看一下堆的可视化操作。
堆的创建
1、堆向下调整
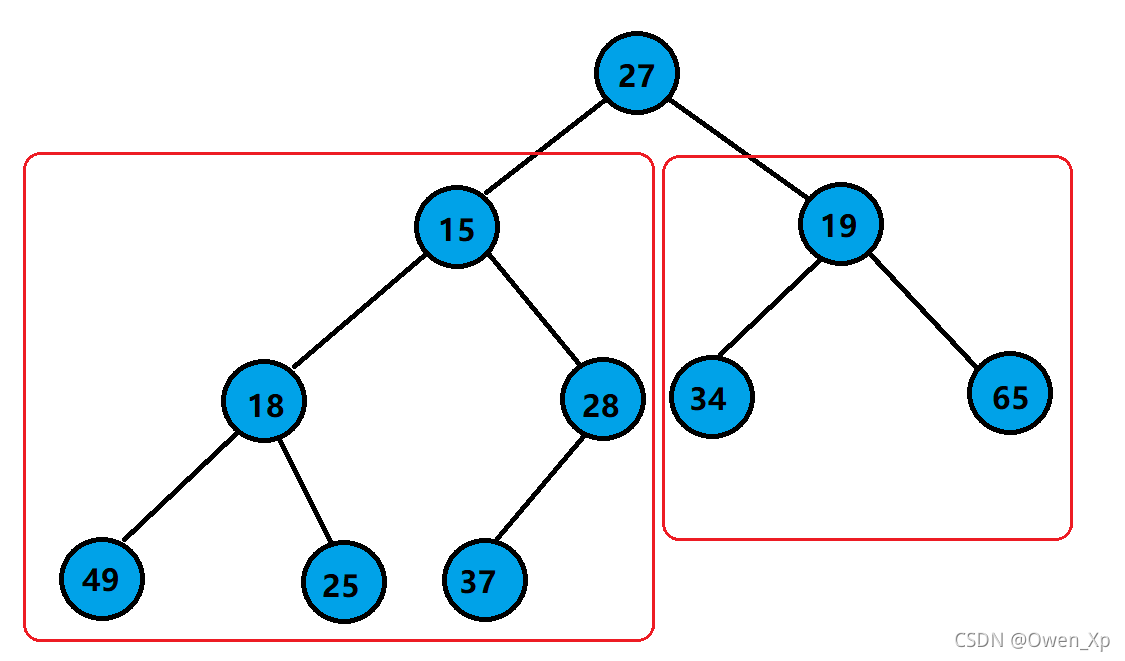
对于集合 { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 } 中的数据,如果将其创建成堆呢?
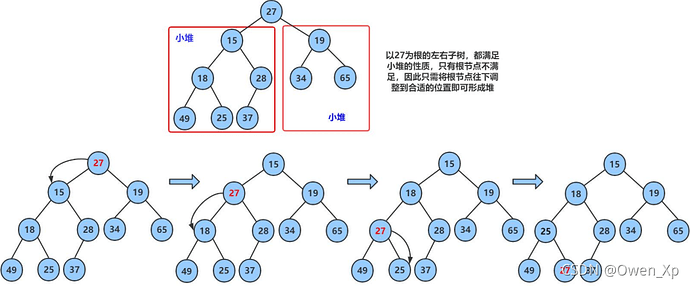
仔细观察上图后发现: 根节点的左右子树已经完全满足堆的性质,因此只需将根节点向下调整好即可 。
向下过程 ( 以小堆为例 ) :
1. 让 parent 标记需要调整的节点, child 标记 parent 的左孩子 ( 注意: parent 如果有孩子一定先是有左孩子 )
2. 如果 parent 的左孩子存在,即 :child < size , 进行以下操作,直到 parent 的左孩子不存在
- parent右孩子是否存在,存在找到左右孩子中最小的孩子,让child进行标记
- 将parent与较小的孩子child比较,如果:parent小于较小的孩子child,调整结束。否则:交换parent与较小的孩子child,交换完成之后,parent中大的元素向下移动,可能导致子树不满足对的性质,因此需要继续向下调整,即parent = child;child = parent*2+1; 然后继续2。
1. public void shiftDown(int[] array, int parent) {
2. // child先标记parent的左孩子,因为parent可能右左没有右
3. int child = 2 * parent + 1;
4. int size = array.length;
5. while (child < size) {
6. // 如果右孩子存在,找到左右孩子中较小的孩子,用child进行标记
7. if(child+1 < size && array[child+1] < array[child]){
8. child += 1;
9. }
11. // 如果双亲比其最小的孩子还小,说明该结构已经满足堆的特性了
12. if (array[parent] <= array[child]) {
13. break;
14. }else{
15. // 将双亲与较小的孩子交换
16. int t = array[parent];
17. array[parent] = array[child];
18. array[child] = t;
20. // parent中大的元素往下移动,可能会造成子树不满足堆的性质,因此需要继续向下调整
21. parent = child;
22. child = parent * 2 + 1;
23. }
24. }
25. }
注意:在调整以 parent 为根的二叉树时,必须要满足 parent 的左子树和右子树已经是堆了才可以向下调整。
时间复杂度分析:
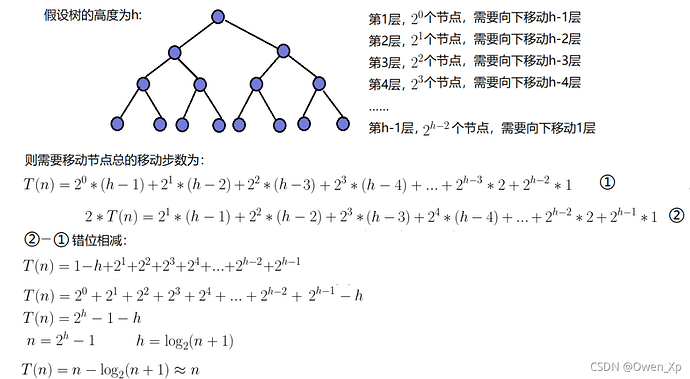
最坏的情况即图示的情况,从根一路比较到叶子,比较的次数为完全二叉树的高度,即时间复杂度为O(log₂N)
2、堆的创建
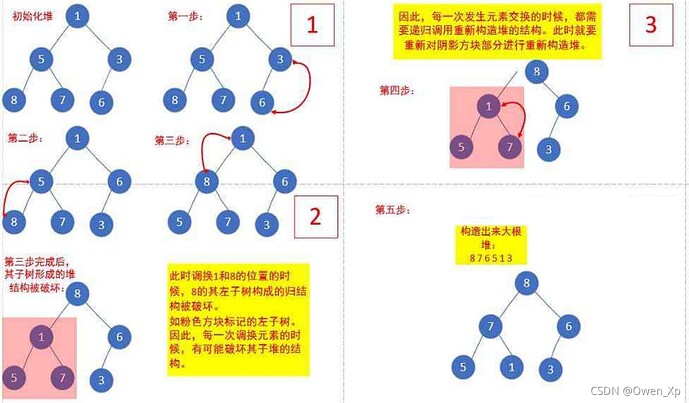
那对于普通的序列 { 1,5,3,8,7,6 } ,即根节点的左右子树不满足堆的特性,又该如何调整呢?
1. public static void createHeap(int[] array) {
2. // 找倒数第一个非叶子节点,从该节点位置开始往前一直到根节点,遇到一个节点,应用向下调整
3. for(int root = (array.length-2)/2; root >= 0; root--){
4. shiftDown(array, array.length, root);
5. }
6. }
3、建堆的时间复杂度
因为堆是完全二叉树,而满二叉树也是完全二叉树,此处为了简化使用满二叉树来证明 ( 时间复杂度本来看的就是近似值,多几个节点不影响最终结果) :
因此:**建堆的时间复杂度为O(N) **
堆的插入和删除
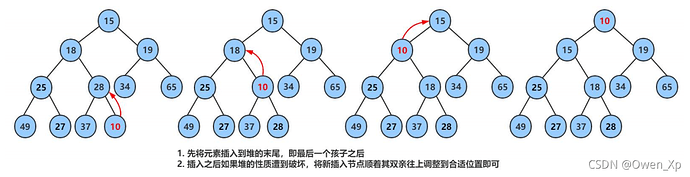
1、堆的插入
堆的插入总共需要两个步骤:
- 先将元素放入到底层空间中(注意:空间不够时需要扩容)
- 将最后新插入的节点向上调整,直到满足堆的性质
1. public void shiftUp(int child) {
2. // 找到child的双亲
3. int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
5. while (child > 0) {
6. // 如果双亲比孩子大,parent满足堆的性质,调整结束
7. if (array[parent] > array[child]) {
8. break;
9. }else{
10. // 将双亲与孩子节点进行交换
11. int t = array[parent];
12. array[parent] = array[child];
13. array[child] = t;
15. // 小的元素向下移动,可能到值子树不满足对的性质,因此需要继续向上调增
16. child = parent;
17. parent = (child - 1) / 2;
18. }
19. }
20. }
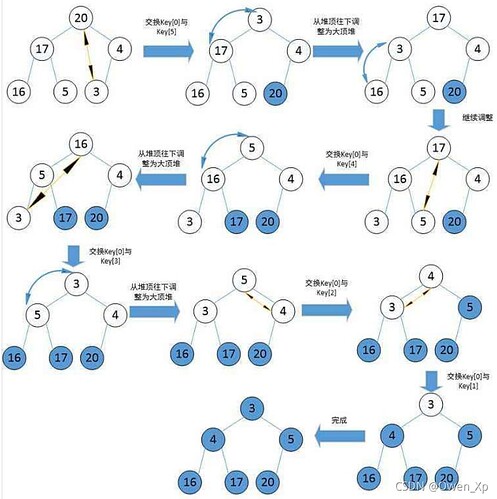
2、堆的删除
堆的删除一定删除的是堆顶元素。
堆的删除步骤如下:
- 将堆顶元素对堆中最后一个元素交换
- 将堆中有效数据个数减少一个
- 对堆顶元素进行向下调整
1. public static void shiftDown(int[] array, int size, int parent){
2. int child = parent*2+1;
4. while(child < size){
5. // 找左右孩子中较大的孩子
6. if(child+1 < size && array[child+1] > array[child]){
7. child += 1;
8. }
10. // 双亲小于交大的孩子
11. if(array[parent] < array[child]){
12. swap(array, parent, child);
13. parent = child;
14. child = parent*2+1;
15. }else{
16. return;
17. }
18. }
19. }
堆的应用
1、优先级队列的实现
用堆作为底层结构 封装优先级队列
1. public class MyPriorityQueue {
2. Integer[] array;
3. int size; // 有效元素的个数
5. public MyPriorityQueue(){
6. array = new Integer[11];
7. size = 0;
8. }
10. public MyPriorityQueue(int initCapacity){
11. if(initCapacity < 1){
12. throw new IllegalArgumentException("初始容量小于1");
13. }
15. array = new Integer[initCapacity];
16. size = 0;
17. }
19. public MyPriorityQueue(Integer[] arr){
20. // 1. 将arr中的元素拷贝到数组中
21. array = new Integer[arr.length];
22. for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i){
23. array[i] = arr[i];
24. }
25. size = arr.length;
27. // 2. 找当前完全二叉树中倒数第一个叶子节点
28. // 注意:倒数第一个叶子节点刚好是最后一个节点的双亲
29. // 最后一个节点的编号size-1 倒数第一个非叶子节点的下标为(size-1-1)/2
30. int lastLeafParent = (size-2)/2;
32. // 3. 从倒数第一个叶子节点位置开始,一直到根节点的位置,使用向下调整
33. for(int root = lastLeafParent; root >= 0; root--){
34. shiftDown(root);
35. }
36. }
38. boolean offer(Integer e){
39. if(e == null){
40. throw new NullPointerException("插入时候元素为null");
41. }
43. ensureCapacity();
45. array[size++] = e;
47. // 注意:当新元素插入之后,可能会破坏对的性质---需要向上调整
48. shiftUp(size-1);
49. return true;
50. }
52. // 将堆顶的元素删除掉
53. public Integer poll(){
54. if(isEmpty()){
55. return null;
56. }
58. Integer ret = array[0];
60. // 1. 将堆顶元素与堆中最后一个元素交换
61. swap(0, size-1);
63. // 2. 将堆中有效元素个数减少一个
64. size--; // size -= 1;
66. // 3. 将堆顶元素往下调整到合适位置
67. shiftDown(0);
68. return ret;
69. }
71. public int size(){
72. return size;
73. }
75. public boolean isEmpty(){
76. return size == 0;
77. }
79. public void clear(){
80. size = 0;
81. }
83. // 功能:调整以parent为根的二叉树
84. // 前提:必须要保证parent的左右子树已经满足堆的特性
85. // 时间复杂度:O(logN)
86. private void shiftDown(int parent){
87. // 默认让child先标记左孩子---因为:parent可能有左没有右
88. int child = parent*2 + 1;
90. // while循环条件可以保证:parent的左孩子一定存在
91. // 但是不能保证parent的右孩子是否存在
92. while(child < size){
93. // 1. 找到左右孩子中较小的孩子
94. if(child+1 < size && array[child+1] < array[child]){
95. child += 1;
96. }
98. // 2. 较小的孩子已经找到了
99. // 检测双亲和孩子间是否满足堆的特性
100. if(array[parent] > array[child]){
101. swap(parent, child);
103. // 大的双亲往下走了,可能会导致子树又不满足堆的特性
104. // 因此需要继续往下调整
105. parent = child;
106. child = parent*2 + 1;
107. }else{
108. // 以parent为根的二叉树已经是堆了
109. return;
110. }
111. }
112. }
114. private void shiftUp(int child){
115. int parent = (child-1)/2;
117. while(child != 0){
118. if(array[child] < array[parent]){
119. swap(child, parent);
120. child = parent;
121. parent = (child-1)/2;
122. }else{
123. return;
124. }
125. }
126. }
128. private void ensureCapacity(){
129. if(array.length == size){
130. int newCapacity = array.length*2;
131. array = Arrays.copyOf(array, newCapacity);
132. }
133. }
135. // 注意:left和right是数组的下标
136. private void swap(int left, int right){
137. int temp = array[left];
138. array[left] = array[right];
139. array[right] = temp;
140. }
2、堆排序
堆排序即利用堆的思想来进行排序,总共分为两个步骤:
1. 建堆
- 升序:建大堆
- 降序:建小堆
2. 利用堆删除思想来进行排序
建堆和堆删除中都用到了向下调整,因此掌握了向下调整,就可以完成堆排序
1. public static void swap(int[] array, int left, int right){
2. int temp = array[left];
3. array[left] = array[right];
4. array[right] = temp;
5. }
7. public static void shiftDown(int[] array, int size, int parent){
8. int child = parent*2+1;
10. while(child < size){
11. // 找左右孩子中较大的孩子
12. if(child+1 < size && array[child+1] > array[child]){
13. child += 1;
14. }
16. // 双亲小于交大的孩子
17. if(array[parent] < array[child]){
18. swap(array, parent, child);
19. parent = child;
20. child = parent*2+1;
21. }else{
22. return;
23. }
24. }
25. }
27. // 假设:升序
28. public static void heapSort(int[] array){
29. // 1. 建堆----升序:大堆 降序:小堆---向下调整
30. for(int root = (array.length-2)/2; root >= 0; root--){
31. shiftDown(array, array.length, root);
32. }
35. // 2. 利用堆删除的思想来排序---向下调整
36. int end = array.length-1; // end标记最后一个元素
37. while(end != 0){
38. swap(array,0,end);
39. shiftDown(array, end,0);
40. end--;
41. }
42. }
3、Top-k问题
TOP-K 问题:即求数据结合中前 K 个最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情况下数据量都比较大 。
对于 Top-K 问题,能想到的最简单直接的方式就是排序,但是:如果数据量非常大,排序就不太可取了 ( 可能数据都不能一下子全部加载到内存中) 。最佳的方式就是用堆来解决,基本思路如下:
1. 用数据集合中前 K 个元素来建堆
- 前k个最大的元素,则建小堆
- 前k个最小的元素,则建大堆
2. 用剩余的 N-K 个元素依次与堆顶元素来比较,不满足则替换堆顶元素
将剩余 N-K 个元素依次与堆顶元素比完之后,堆中剩余的 K 个元素就是所求的前 K 个最小或者最大的元素。
1. class Solution {
2. public int[] smallestK(int[] arr, int k) {
3. int[] vec = new int[k];
4. if (k == 0) { // 排除 0 的情况
5. return vec;
6. }
7. PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
8. public int compare(Integer num1, Integer num2) {
9. return num2 - num1;
10. }
11. });
12. for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
13. queue.offer(arr[i]);
14. }
15. for (int i = k; i < arr.length; ++i) {
16. if (queue.peek() > arr[i]) {
17. queue.poll();
18. queue.offer(arr[i]);
19. }
20. }
21. for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
22. vec[i] = queue.poll();
23. }
24. return vec;
25. }
26. }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(nlog k),其中 n 是数组 arr 的长度。由于大根堆实时维护前 k 小值,所以插入删除都是O(logk) 的时间复杂度,最坏情况下数组里 n 个数都会插入,所以一共需要 O(nlogk) 的时间复杂度。
空间复杂度:O(k),因为大根堆里最多 k 个数